アプリ(入力モードをハックする)
Top
 インストール
インストール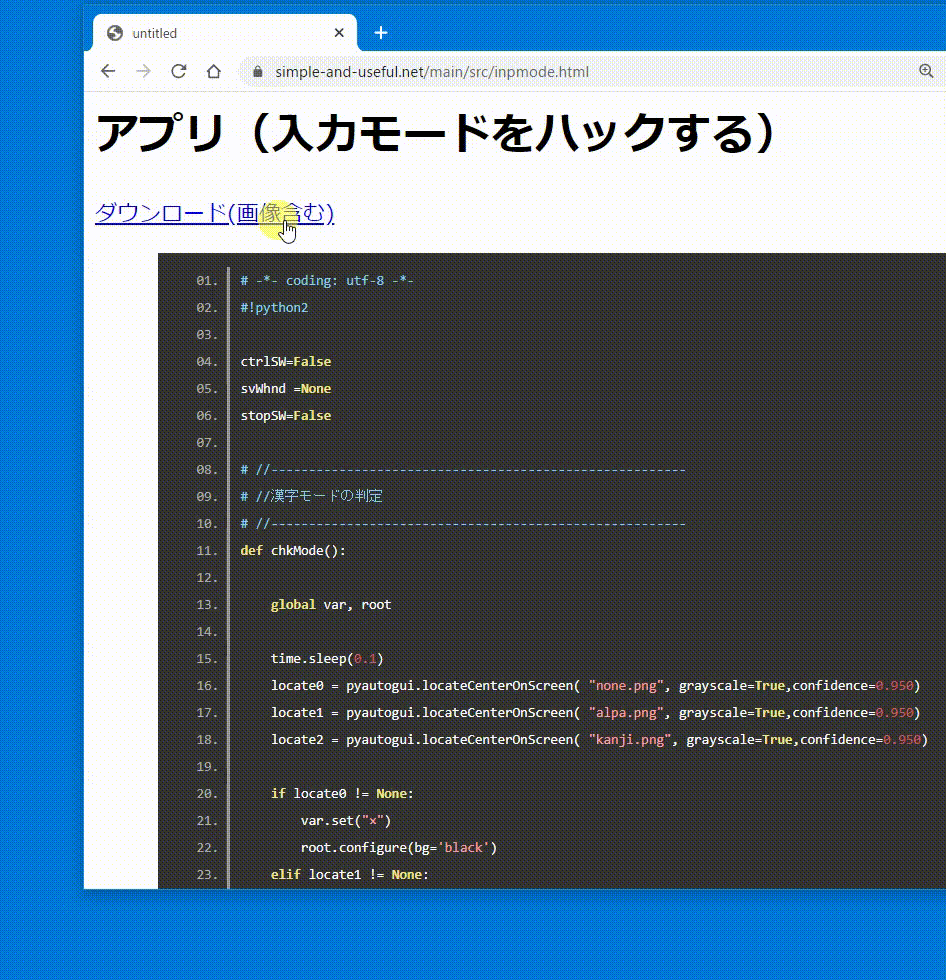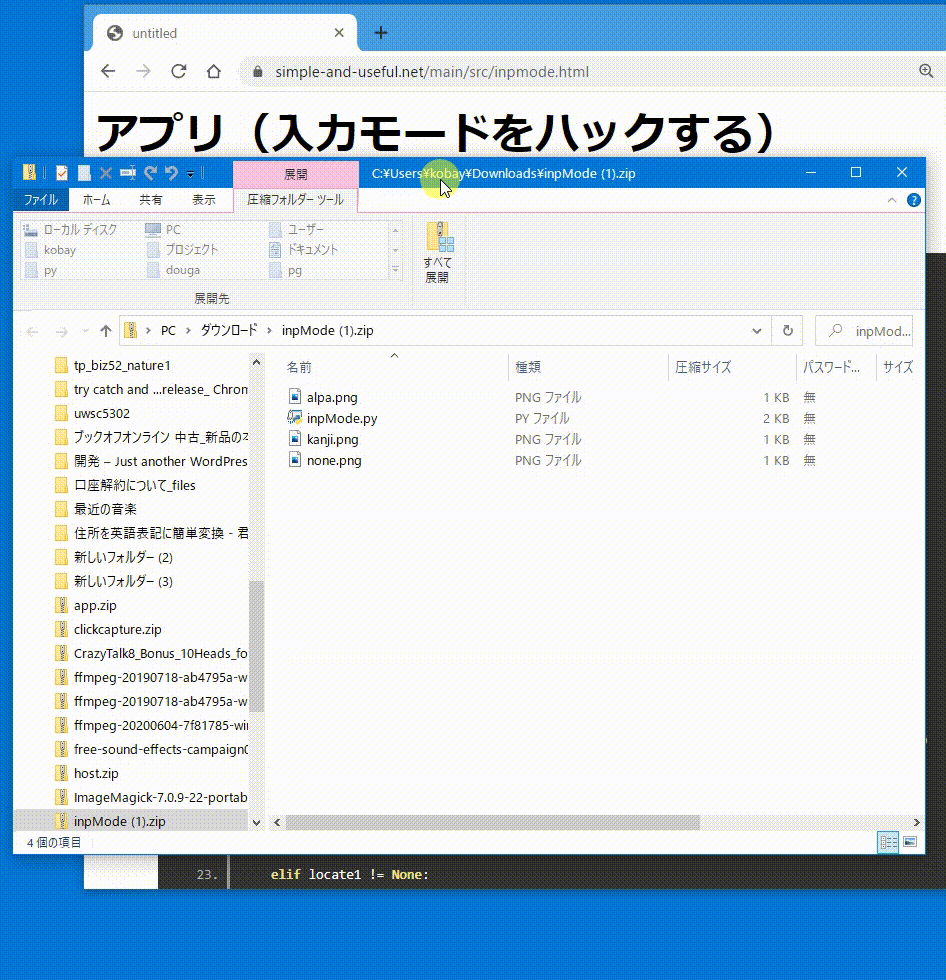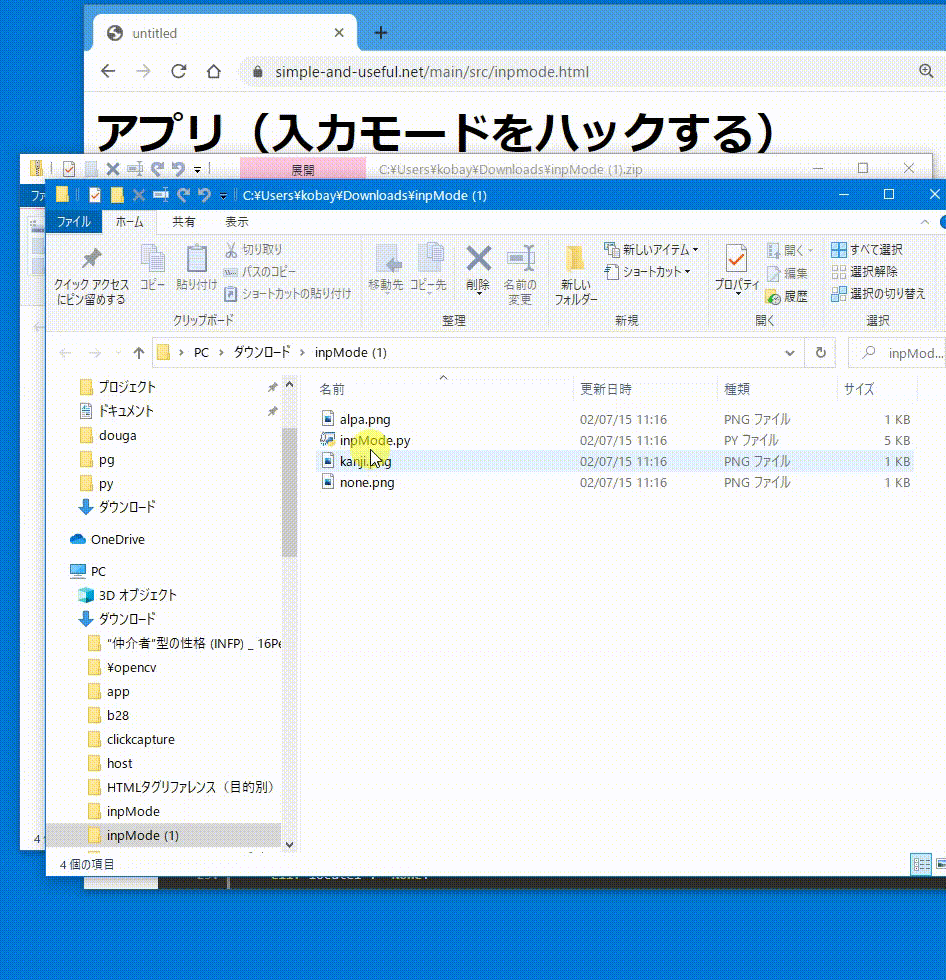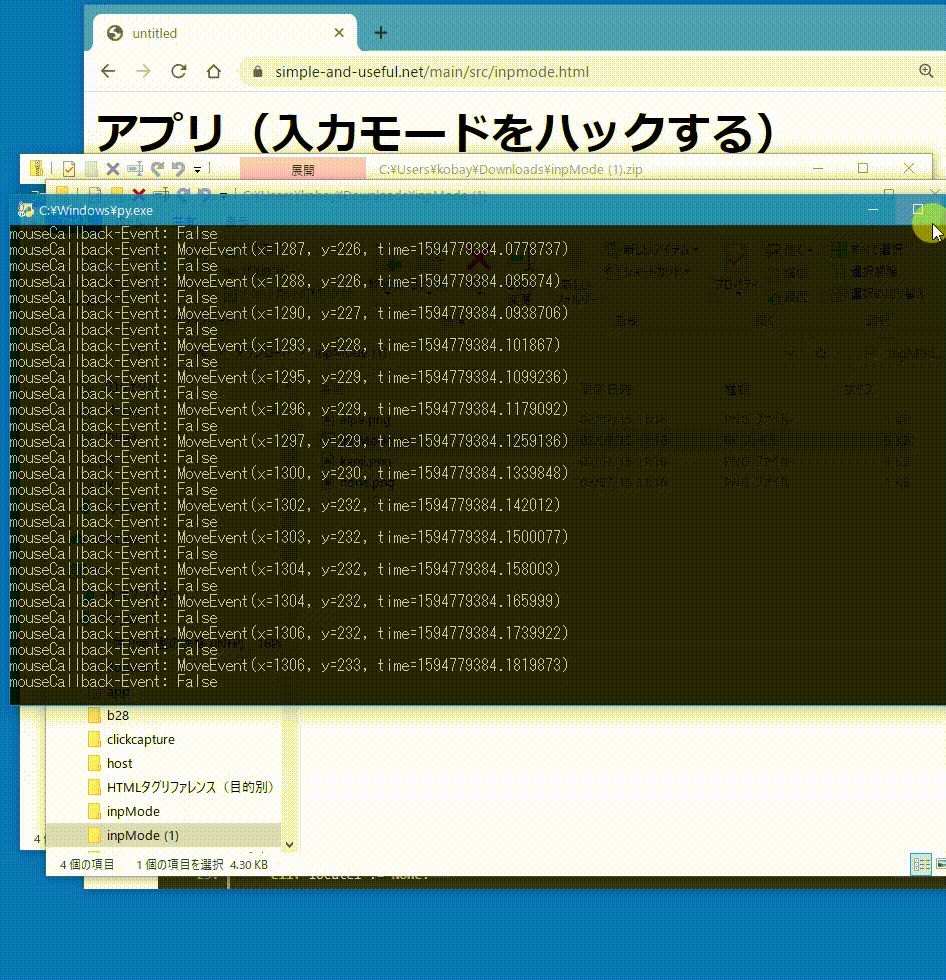
Python #1 入力モードをハッキングするアプリ
Pythonでアプリを作成してみよう、
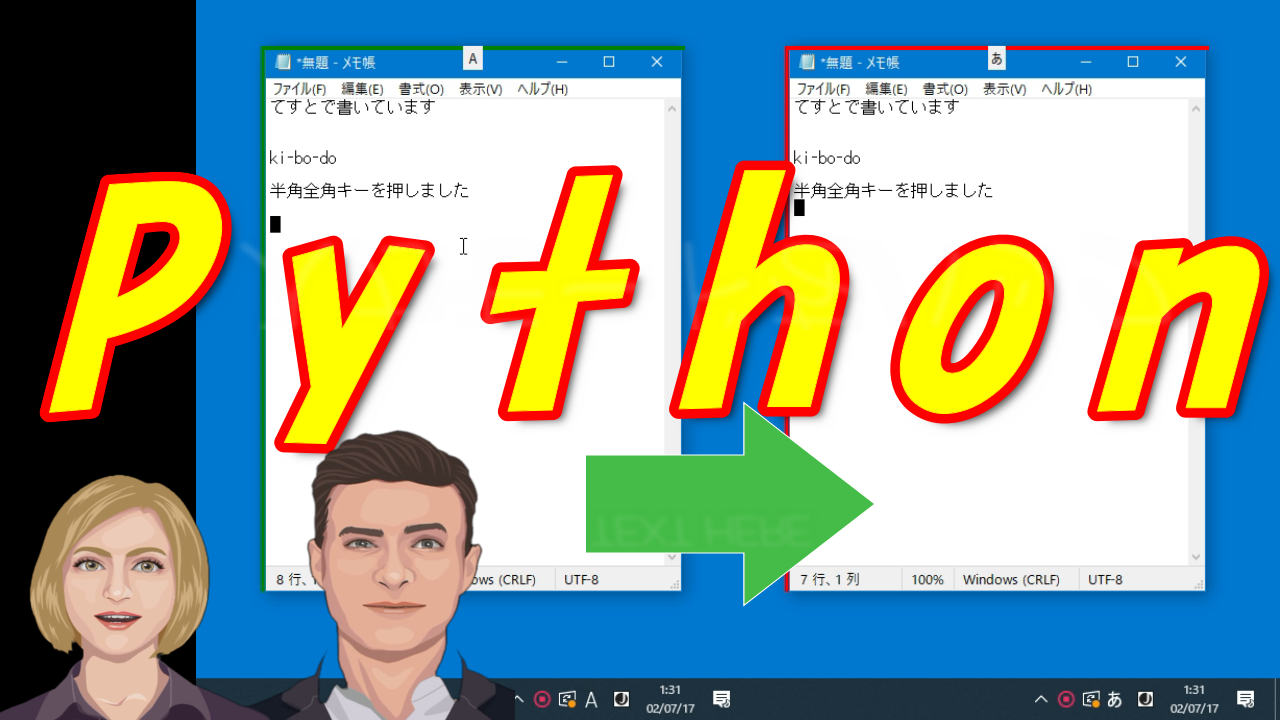
入力モード(半角/全角)をウインドウ枠の色で判別するアプリです。
判定には、PyAutoGuiのlocateOnScreenを使用、
すべての解説はできませんので、ソースコードをアップします。
見てみて下さいね!
https://simple-and-useful.net/main/src/inpmode.html
機能について
ウインドウをクリックして選択すると、ウインドウ枠が表示され、
この色によって現在漢字モードかどうかを識別することができます。
コントロールキーを押しながらウインドウをクリックすると、
ウインドウ枠に色が付きます。
終了は、上のラベル「あ、A、*」をクリックです。
デスクトップ、タスクバーをクリックすると、画面の左上に小さく表示されます。
使用するモジュール
Tkinter
クロスプラットフォームなGUIライブラリ
PyAutoGUI
マウスやキーボード操作の自動化
win32api,win32gui
PythonでWindowsのAPIを可能にする
mouse,keyboard
マウス操作をフックして監視したり、
マウス操作を行う事もできます
-----------------------------------
画像位置を取得する
モジュール PyAutoGui
座標位置 = locateOnScreen
( "none.png",
grayscale=True,
confidence=0.950,
region=(0,0, 1920,1080 )
)
-----------------------------------
次は、入力モードの判定ですね!
locateOnScreenは、\n画面から指定画像の位置を求めるもので、
画像が一致しない場合は、Noneが返ります
これで漢字モードがどうかを判定しています。
引数には、\ngrayscale、confidence、regionが、
あります。
fgrayscaleやregionでスピードUPできます
動画の字幕
整理されていませんが、何かお役に立てば!
$100
-----------------------------------
入力モードをハッキング
-----------------------------------
f入力モードをハッキング
漢字変換モードを判定して、\n見やすくするアプリを作ってみましょう!
$200
-----------------------------------
[入力モード判定アプリ]
-----------------------------------
チョットこれを見てくださいね
アプリを起動すると左上に小さいラベルが出てきます
コントロールキーを押しながら、ウインドウをクリックします
f何かでましたね
このウインドウ枠の色で判定ができますよ
切替えてみますね
fいいですね、赤が漢字モードかぁ
終わりにしたい時は、ここをクリックします
$300
-----------------------------------
漢字入力モードかを判定する
-----------------------------------
今回は、このアプリを作ってみましょう!
f漢字入力モードかを判定するアプリですね
ソースファイルをネット上に上げてありますので、
参考にしてみて下さい
f変更して自分好みしたいです
是非、頑張ってね!
#98 0.5 1,97 0.8 0.5
$400
----------------------------------------------
アプリの仕組み
ウインドウがクリックされたら
コントロール押下をチェックして
ウインドウ枠を表示
半角/全角キーが押されたら、
入力モードを調べて
ウインドウ枠の色を反映させる
----------------------------------------------
fプログラムは、どのようになっているのですか?
マウスとキーボードをフックして監視します。
マウスのクリックとコントロールキーをチェックして、
クリックされたウインドウに枠を表示させます
半角/全角キーが押されたら、
今の入力モードを調べて、
モードによりウインドウの枠色を変えています。
f大変そうだなぁ
色々なモジュールを使用して実現させてまぁ~す
$500
-----------------------------------
使用するモジュール
Tkinter
クロスプラットフォームなGUIライブラリ
PyAutoGUI
マウスやキーボード操作の自動化
win32api,win32gui
PythonでWindowsのAPIを可能にする
mouse,keyboard
マウス操作をフックして監視したり、
マウス操作を行う事もできます
-----------------------------------
使用するモジュールの説明をします
fTkinter
クロスプラットフォームなGUIライブラリですね
Windows,Mac,Linuxでも動きます
fウインドウを作成したい時に使うのですね
fPyAutoGUI
マウスやキーボード操作の自動化ができるモジュールです
画像認識ができるので便利です
fwin32api,win32gui
PythonでWindowsのAPIを使う事ができるモジュールです
fmouse,keyboard
よくある名前で迷いそうですが、これはモジュールですよ
マウス(キーボード)操作をフックして監視したり、
マウス(キーボード)の操作を行う事もできます
f操作の自動化ですね
#98 0.5 1,97 1 0.8
$600
-----------------------------------
Tkinter
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.geometry('20x20+0+0')
root.overrideredirect(True)
root.wm_attributes("-topmost", True)
root.configure(bg='white')
root.wm_attributes(
"-transparentcolor", "white")
-----------------------------------
Tkinterは、ウインドウ表示ができる\nGUIのモジュールです
今回は、透明なウインドウ枠を表示しています
fウインドウとは、思えなかったですねぇ~
では順番に、
ウインドウの位置とサイズ
f幅、高さ、X座標、Y座標
ウインドウのタイトルバーを消しています
ウインドウを最前面に表示
fあっ、いつも上に表示されて邪魔な奴にするのですね
いゃいゃいゃ
最後は背景色の設定とウインドウを透明にします
#98 0.5 1,97 1 0.6
$700
-----------------------------------
ラベルの設定
var = tkinter.StringVar()
var.set("*")
lbl = tkinter.Label(root, textvariable=var )
lbl.pack( anchor ="s")
※処理中に、「var.set("??")」で変更が可能
-----------------------------------
ラベルを変更する場合は、ちょっと面倒かもしれないね
fStringVarで作成したオブジェクトにsetすれば、\n変更できるのですね。
ラベルに固定文字を表示するだけなら、簡単なんだけどね!
#98 0.5 1.0,97 1 0.9
$800
-----------------------------------
入力操作の監視
バックグラウンドで、マウス操作を取得
mouse.hook( mouseCallback )
(キーボード操作取得)
keyboard.hook( keyCallback )
-----------------------------------
f入力操作の監視ですね
このメソッドは、バックグランドでマウスの操作を
取得する優れもんだよ
fそぅかぁ~、普通アプリは自分で\nイベントを処理しているもんね
そう、裏で盗み見ているような感じかなぁ~
引数には、呼び出される関数を書いてくださいね
f呼びだされるのかぁ~
マウス操作があったら、呼び出されますよ!
$900
-----------------------------------
キーボード操作を監視
def keyCallback( event ):
if "ctrl" == event.name:
if "up" == event.event_type:
ctrlSW =False
print("ctrlSW", ctrlSW)
else:
ctrlSW =True
print("ctrlSW", ctrlSW)
#バックグラウンドで、キーボード操作を取得
keyboard.hook( keyCallback )
-----------------------------------
実際のコードで見てみましょう
event.nameがキーの種類で、
event.event_typeがキーの状態です
キーの状態とは、押されている、放されたがわかります
fこの関数は、コントロールキーが押されているかが、
fわかるのですね
hookは1回だけ書けば良いですからね
fキーボード操作があったら\n呼び出されるのですね
#97 1 0.8
$1000
-----------------------------------
画像位置を取得する
モジュール PyAutoGui
座標位置 = locateOnScreen
( "none.png",
grayscale=True,
confidence=0.950,
region=(0,0, 1920,1080 )
)
-----------------------------------
f次は、入力モードの判定ですね!
はい
locateOnScreenは、\n画面から指定画像の位置を求めるもので、
画像が一致しない場合は、Noneが返ります
fこれで漢字モードがどうかを判定しているのですね
はい、そうですね
引数には、\ngrayscale、confidence、regionが、
あります。
調整が必要ですね
fgrayscaleやregionでスピードUPできますね、
f最適なものを求めなきゃ!
ダウンロード(画像含む)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#!python2
ctrlSW=False
svWhnd =None
# //-------------------------------------------------------
# //漢字モードの判定
# //-------------------------------------------------------
def chkMode():
global var, root, canvas
time.sleep(0.1)
# //locate0 = pyautogui.locateCenterOnScreen( "none.png", grayscale=True,confidence=0.950)
# //locate1 = pyautogui.locateCenterOnScreen( "alpa.png", grayscale=True,confidence=0.950)
# //locate2 = pyautogui.locateOnScreen( "kanji.png", grayscale=True,confidence=0.950, region(xx-100,yy-50,xx,yy))
locate2 = pyautogui.locateOnScreen('kanji.png', grayscale=True,confidence=0.8,region=(xx-200,yy-50, xx,yy ))
# //if locate0 != None:
# //var.set("×")
# //root.configure(bg='black')
# //elif locate1 != None:
# //var.set("A")
# //root.configure(bg='green')
# //elif locate2 != None:
# //var.set("あ")
# //root.configure(bg='red')
# //else:
# //var.set("*")
# //root.configure(bg='white')
haba = 4
if locate2 != None:
var.set("あ")
# //root.configure(bg='red')
col ="red"
canvas.create_rectangle(haba, haba, tarW, tarH, outline= col, width="%d" %haba)
else:
var.set("A")
# //root.configure(bg='green')
col ="green"
canvas.create_rectangle(haba, haba, tarW, tarH, outline= col, width="%d" %haba)
def timer():
try:
chkMode()
except Exception as e:
print(e )
root.after(1000, timer)
# //-------------------------------------------------------
# //キー入力のイベント
# //-------------------------------------------------------
'''
チェックするキー
コントロールキー
半角/全角
'''
def keyCallback( event ):
global ctrlSW
print( event )
if "半角/全角" == event.name and "down" == event.event_type:
# //if "半角/全角" == event.name:
chkMode()
if "ctrl" == event.name:
if "up" == event.event_type:
ctrlSW =False
print("ctrlSW", ctrlSW)
else:
ctrlSW =True
print("ctrlSW", ctrlSW)
# //-------------------------------------------------------
# //マウスのイベント
# //-------------------------------------------------------
def mouseCallback( event ):
global ctrlSW,root,svWhnd, tarW, tarH
# //print('mouseCallback-Event:', event )
# //print('mouseCallback-Event:', type(event) == mouse.ButtonEvent )
whnd = win32gui.WindowFromPoint(win32api.GetCursorPos() )
textName = win32gui.GetWindowText(whnd)
className = win32gui.GetClassName(whnd)
# //print( "textName", textName)
# //print( "className", className)
if "CiceroUIWndFrame" == className:
time.sleep(0.2)
chkMode()
return True
if type(event) == mouse.ButtonEvent:
px,py = pyautogui.position()
# //if event.event_type == "down" and event.button=="left":
# //rect = win32gui.GetWindowRect(whnd)
# //x = rect[0]
# //y = rect[1]
# //"""
# //int cxSizeFrame = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXSIZEFRAME); // 境界線幅X方向
# //int cySizeFrame = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYSIZEFRAME); // 境界線幅Y方向
# //int cyCaption = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYCAPTION); // タイトルバーの高さ
# //"""
# //capH = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(win32con.SM_CYCAPTION)
# //kyoY = win32api.GetSystemMetrics(win32con.SM_CYSIZEFRAME)
# //ttlH = capH + (kyoY*2)
# //print("ttlH=",ttlH)
# //if (px >x and px < rect[2]) and ctrlSW==False:
# //if py > y and py < y+ ttlH:
# //root.geometry( "20x20+0+0" )
# //canvas.create_rectangle(5, 5, tarW, tarH, outline= "white", width="5")
# //svWhnd = None
# //return
if event.event_type == "up" and event.button=="left":
# //print("event_type", event.event_type )
# //print("button", event.button )
whnd = win32gui.WindowFromPoint(win32api.GetCursorPos() )
textName = win32gui.GetWindowText(whnd)
className = win32gui.GetClassName(whnd)
# //print( "textName", textName)
# //print( "className", className)
if className == "Static":
# //tkinter.messagebox.showinfo("終了", "終了します")
root.quit()
sys.exit()
"""
if className == "TkChild":
print("TkChild")
# //pyautogui.hotkey('hanja')
# //chkMode()
return
"""
if className == "MSTaskListWClass" or className == "SHELLDLL_DefView":
# //if className == "SHELLDLL_DefView":
root.geometry( "20x20+0+0" )
canvas.create_rectangle(5, 5, tarW, tarH, outline= "white", width="5")
svWhnd = whnd
return False
"""
if className == "IMEModeButton":
time.sleep(0.1)
chkMode()
return
"""
rect = win32gui.GetWindowRect(whnd)
x = rect[0]
y = rect[1]
if svWhnd == whnd:
time.sleep(0.2)
chkMode()
else:
if ctrlSW:
canvas.create_rectangle(5, 5, tarW, tarH, outline= "white", width="5")
tarW = rect[2]-x
tarH = rect[3]-y
root.geometry( "%dx%d+%d+%d" %(tarW-7,tarH-7, x+3, y) )
# //root.geometry( "10x20+10+10")
# //time.sleep(0.5)
chkMode()
svWhnd = whnd
return True
import time,os,sys
import tkinter as tkinter
import mouse
import keyboard
import pyautogui
import win32gui
import win32api
import win32con
xx, yy = pyautogui.size()
print(xx,yy)
# //メインウインドウ用
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.geometry('20x20+0+0')
root.overrideredirect(True)
root.wm_attributes("-topmost", True)
root.configure(bg='white')
root.wm_attributes("-transparentcolor", "white")
tarW =xx
tarH =yy
canvas = tkinter.Canvas(root, width=tarW, height=tarH, bg="white")
canvas.place(x=-2, y=-2)
#ラベル
var = tkinter.StringVar()
var.set("*")
lbl = tkinter.Label(root, textvariable=var )
lbl.pack( anchor ="s")
# //timer()
mouse.hook( mouseCallback )
keyboard.hook( keyCallback )
# //root.iconbitmap(default='/Users/kobay/Downloads/left.ico')
root.mainloop()
©2022 Kenji Kobayashi
YouTube
 インストール
インストール